Heat Exchangers Inspection
Eddyfi Technologies for Heat Exchangers Inspection Applications
The inspection of heat exchangers encompasses the assessment of the tubes found in a variety of assets including shell-and-tube heat exchangers, steam generators, boilers, coolers, feedwater heaters, and condensers. The most common defect that asset owners and inspection companies search for are pitting and corrosion, longitudinal cracks, circumferential cracks especially at the tubesheet, erosion, fretting and metal loss. Detecting these defects early enables optimal performance and of course the prevention of critical failure.
Details
The inspection of heat exchangers encompasses the assessment of the tubes found in a variety of assets including shell-and-tube heat exchangers, steam generators, boilers, coolers, feedwater heaters, and condensers. These key assets are common in the oil, gas, petrochemical, power generation and nuclear industries. Heat exchanger tubes are typically small in diameter and numerous, some bundles containing as few as five tubes while others as many as 50,000. Tubing can be straight or curved, and typically require specific probes to inspect from the inside of the tube.
The most common defect that asset owners and inspection companies search for are pitting and corrosion, longitudinal cracks, circumferential cracks especially at the tubesheet, erosion, fretting and metal loss. Detecting these defects early enables optimal performance and of course the prevention of critical failure. No individual non-destructive testing (NDT) technique is adequate for all tubing applications, types of materials and defects.
Ferrous Tubing
Ferrous tubes are common in the shell-and-tube heat exchangers of the oil, gas, and petrochemical industry, among others, where inspection companies typically use RFT, NFT, NFA, MFL, and IRIS in various combinations to detect corrosion, pitting, cracking, and erosion in the tubes to maintain efficiency. The generally poor cleanliness of tubes means that probes must be durable and reliable, while the dynamics of the industry – including unplanned work – calls for short lead times. This is exactly what Eddyfi Technologies offers. And, when our standard probes don’t meet application requirements, we are fully equipped to custom design and manufacture special probes.
Non-Ferrous Tubing
Non-ferrous metals, like Inconel, are used to make tubes that are non-magnetic and offer a better resistance to corrosion and stress cracking. They are necessary in the power generation and nuclear industries due to the critical nature of the systems they are part of, such as steam generators in nuclear plants. They are also omnipresent in the balance of plants (BoP) of such industries. Eddy currents are used in these industries because they are perfectly suited to inspecting non-ferrous alloys. Our high-performance probes are designed to offer excellent signals while being very durable. Operators can inspect a large number of tubes rapidly and precisely.
Eddyfi Technologies offers a multiplexed eddy current array tubing probe for detecting, sizing and positioning circumferential cracks in the vicinity of the tubesheet of non-ferromagnetic heat exchanger tubes. It offers rapid assessment of circumferential cracks in the most challenging location with full 3D imaging for easier interpretation. This cracking is common on heat exchanger components including power plant feedwater heaters and condensers, and petrochemical refinery heat exchangers.
The Eddyfi Ectane®, configurable for any type of inspection technique, Magnifi acquisition and analysis software, and our patented Eddyfi DefHi ECA probe are a complete system for flaw detection and characterization, discriminating against unwanted signals like those from tubesheets and roll transition.
Compared to standard ECT bobbin probes, this solution differentiates the various complex geometries inside heat exchanger tubing to enable accurate detection, measurement and characterization of small volume circumferential cracks.
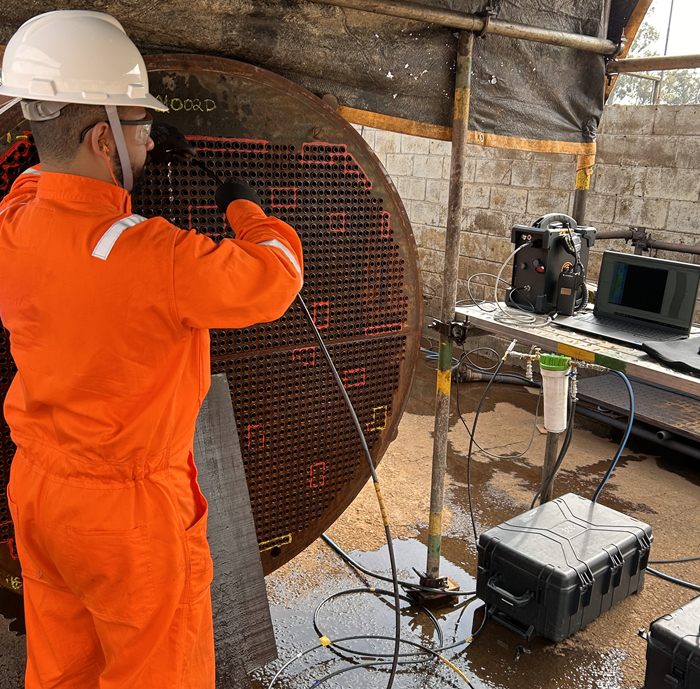

NDT of Heat Exchanger Shells
In order to determine remaining life assessments, ultrasonic corrosion mapping of the inlet end of a heat exchanger is imperative. This risk-based assessment promotes maintenance programs and ideal repair strategies. Eddyfi Technologies is offering a solution that allows in-service examinations.
The Eddyfi Technologies Automated ultrasonic corrosion mapping solution offers remote access capabilities that remove operators from the hazardous areas requiring inspection, components capable of operating on the elevated surface temperatures, and a narrow water column so water could be recycled at a rate that prevents it from boiling at the test surface before ultrasonic propagates into the heat exchanger. The robotic solution provides consistent inspection data that enables operators and asset owners to make informed maintenance decisions.

Many heat exchanger shells are either insulated or come with a fire protection coating. Therefore, it is not uncommon to see corrosion mechanisms at play: moisture is often trapped between the steel (outer diameter) and the insulation/fireproofing material, leading to what the industry calls “Corrosion Under Insulation”. The threat can be significant because corrosion is impossible to detect unless the asset is taken out of service, entire insulation/fireproofing removed, and visual inspection performed. Eddyfi Technologies offers a solution that allows detecting corrosion in this scenario, without having to disrupt operations. Lyft® is a Pulsed Eddy Current (PEC) solution capable of locating generalized corrosion through insulation/coating.

We offer a range of advanced NDT solutions specifically designed for heat exchanger inspection applications. Contact our friendly and knowledgeable team to discuss your requirements.
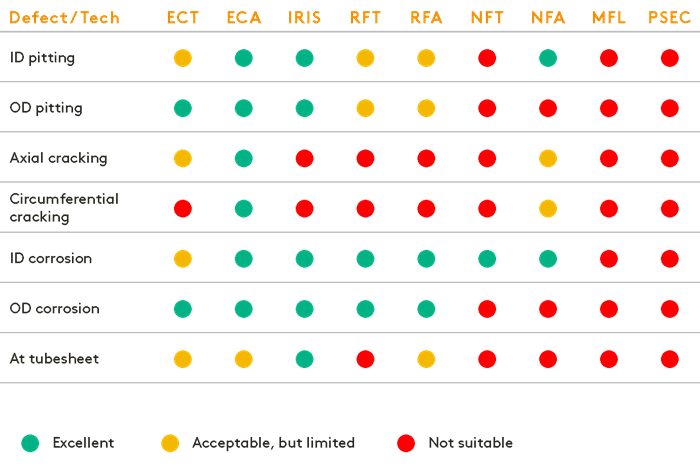
Tube Testing Technique Suitability According to Material
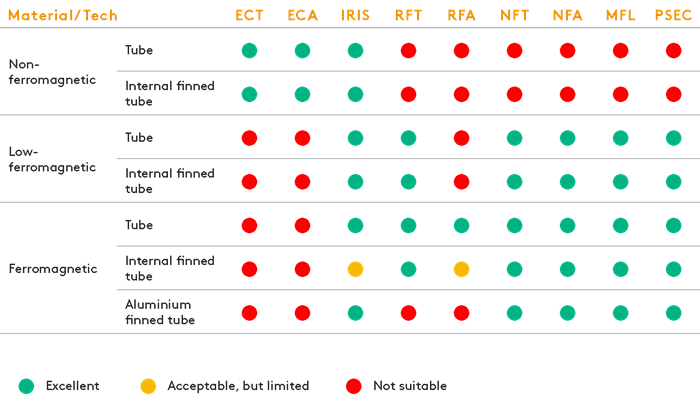
Tube Testing Detection Capabilities According to Defect Type
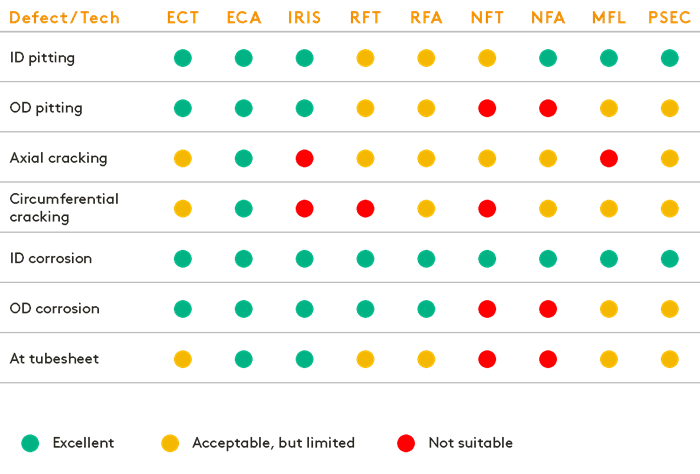
Tube Testing Sizing Capabilities According to Defect Type