Standardizing Guided Wave Testing Methods and the Role of Sonyks™
Ask an expertGuided wave testing (GWT) was developed in the 1990s for detecting corrosion in pipelines, with the first products released in the early 2000s. Following well-defined procedures and international standards such as ISO 9690, GWT has proven to be a reliable inspection technique for identifying corrosion defects, balancing sensitivity (5% cross-sectional area loss) and range [up to 30 meters (100 feet) on typical above-ground pipe]. Recent advancements in guided wave technology necessitate a better standardization of the method and clarification of terminology to differentiate it from other ultrasonic wave methods. This application note aims to define GWT using test frequency as the primary differentiator.
The Challenge
Standardize and clarify the language around guided wave testing to differentiate it from other methods using ultrasonic waves.
Guided wave testing on pipelines employs low-frequency ultrasound (approximately 20-200kHz) to detect corrosion by propagating sound axially along the pipe. Changes in the pipe's cross-section cause sound reflections back to the tool, allowing for the detection of defects without probes needing to be directly over the inspection area. Despite its value in productivity and unique inspection capability, the broad term "Guided Wave Testing" has become too vague for specific pipeline inspections. There is a need to separate GWT into distinct categories to prevent confusion.
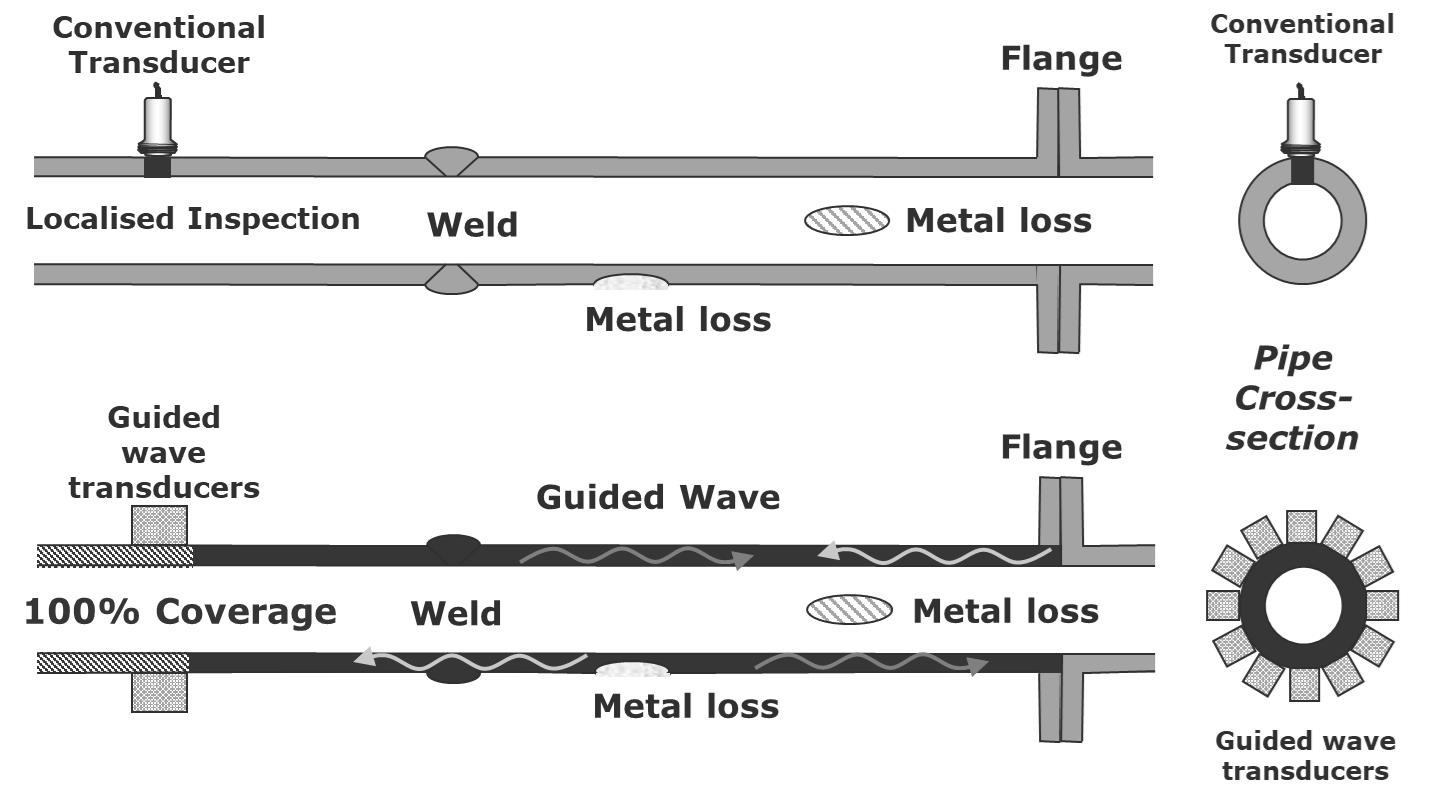
Figure 1:
Comparing GWT to conventional NDT methods showing that the metal loss can be found without the tool being located directly over the metal loss.
The Solution
Categorize guided wave testing into three subcategories based on frequency: Long-Range Ultrasonic Testing (LRUT), Medium-Range Ultrasonic Testing (MRUT), and Short-Range Ultrasonic Testing (SRUT).
To address this, GWT in pipelines can be divided into three subcategories based on frequency: Long-Range Ultrasonic Testing (LRUT), Medium-Range Ultrasonic Testing (MRUT), and Short-Range Ultrasonic Testing (SRUT). Each subcategory is defined as follows:
| Subcategory | Frequency Range | Expected Test Range | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long Range Ultrasonic Testing | <100kHz (usually 20-80kHz) | 10s of metres | 5% Cross-sectional area |
| Medium Range Ultrasonic Testing | 100-200kHz (usually 110-150kHz) | Up to 12m | 1% Cross-sectional area |
| Short Range Ultrasonic Testing | >200kHz (usually scanning-based technologies) | 1-2m | Dependent on application |








